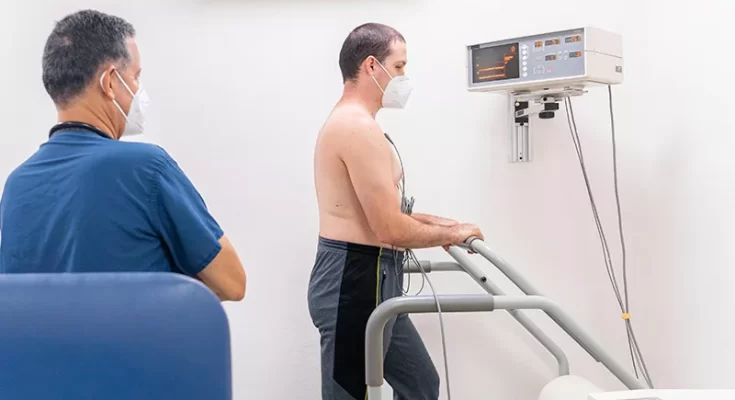
Understanding cardiac health often feels overwhelming. One common procedure is the cardiac stress test. It helps assess how the heart works under pressure. By measuring heart function during physical activity—like walking on a treadmill or cycling—a stress test can reveal important information. Much like mapping the intricate network of veins Manhattan, this test uncovers hidden pathways and potential blockages. It’s a simple yet vital tool for ensuring a healthy heart.
What is a Cardiac Stress Test?
A cardiac stress test is a method used to gauge how well your heart handles physical exertion. It involves monitoring heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing while engaging in exercise. Some tests use medication to mimic exercise effects. This provides a comprehensive view of heart performance and can help identify any underlying issues.
Types of Stress Tests
There are several types of stress tests available:
- Treadmill Test: You walk or run on a treadmill while your heart activity is monitored.
- Stationary Bike Test: Similar to the treadmill test but using a stationary bike.
- Pharmacologic Stress Test: Involves medication when physical activity isn’t possible.
Why Cardiac Stress Tests Matter
The significance of cardiac stress tests lies in their ability to detect problems early. They are crucial for diagnosing conditions like coronary artery disease. By ensuring timely intervention, these tests can prevent more serious complications. Beyond diagnosis, stress tests also aid in developing treatment plans suited to individual needs.
How a Stress Test Works
During a stress test, electrodes are attached to your chest to monitor your heart’s electrical activity. As you exercise, the intensity gradually increases. Medical staff observe your heart’s behavior and note any irregularities. After the test, you will cool down, and the results will be analyzed.
Comparison: Exercise vs. Pharmacologic Stress Test
| Aspect | Exercise Stress Test | Pharmacologic Stress Test |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Physical exercise (treadmill/bike) | Medication-induced heart stress |
| Duration | 30-60 minutes | Approximately 1 hour |
| Ideal for | Those able to perform physical activity | Individuals unable to exercise physically |
Preparing for a Stress Test
Before the test, you might need to avoid eating, drinking, or taking certain medications. Comfortable clothing and shoes for exercise are recommended. It’s important to consult with your doctor about any specific preparations.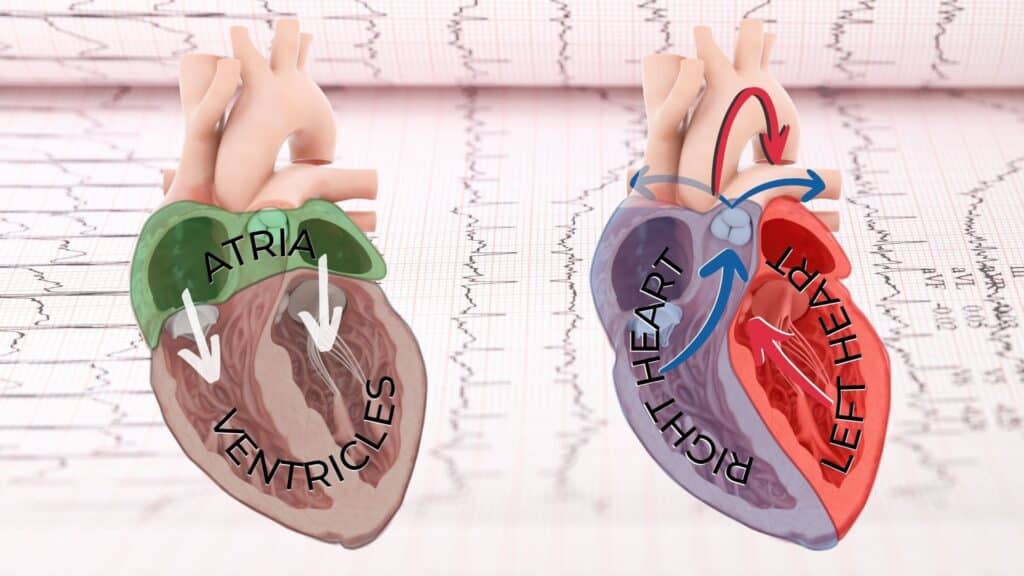
Interpreting Stress Test Results
The results help determine if your heart receives enough blood and oxygen during activity. They can uncover abnormal heart rhythms and identify areas where blood flow is limited. Your doctor will discuss these findings and recommend further actions if needed. More detailed information can be found on the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute’s website.
Benefits of Cardiac Stress Tests
Stress tests not only diagnose heart conditions but also provide insight into your overall cardiovascular health. They can guide treatment plans, assess the effectiveness of cardiac procedures, and ensure that exercise regimens are safe. The test is a proactive measure to maintain heart health and avoid potential heart issues.
Conclusion
Cardiac stress tests are essential tools in the realm of heart health. Simple yet effective, they offer critical insights into heart performance and can guide necessary medical interventions. Understanding the role of stress tests in maintaining cardiac wellness empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health. Regular evaluations and consultations with healthcare providers can ensure a proactive approach to heart health.